For the latest information, see the documentation.
Reasons for defects in point clouds:
- Weak specular reflection
- Strong specular reflection
- A combination of the two reasons above
Below are examples of the second reason: strong specular reflection
Problem
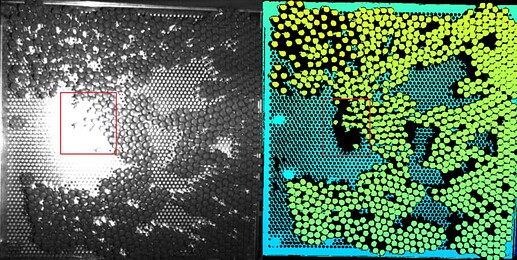
Defective point clouds in the center of the captured image.
Example
Below are two pictures of ampoules on a glass work table. The camera captures the scene from above the table vertically. From the flash image, it is clear that strong specular reflection results in defective point clouds.
Left: The flash image.
Right: The depth map.
Solutions
- Reduce projection light and avoid over-exposure.
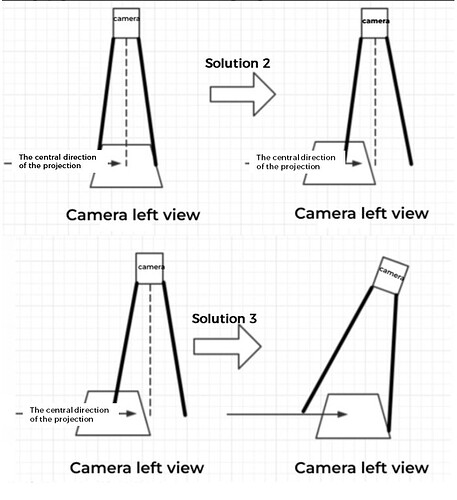
- Move the camera horizontally to reduce specular reflection.
- Position the camera appropriately to capture the entire scene.
Effect
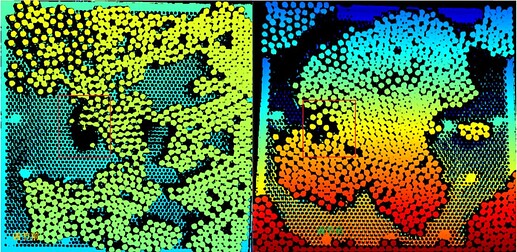
Left: The depth map before adjustments.
Right: The depth map after adjustments.
After adjustments, depth map information loss (in the red frame) is avoided.
Passive solution
If the camera mount is currently restricted, you can try adjusting the camera exposure to see if it can completely solve the existing point cloud issues.
Here are the main adjustment approaches:
- Decrease the camera’s exposure intensity. You can reduce the 3D exposure, as well as lower the laser and projection light intensities. This method can address the issue of over-exposure at the current position, although it may result in under-exposure in the surrounding areas.
- Add an additional set of high exposure settings to accommodate the darker parts in the current scene.
- Ultimately, the parameter adjustment issue can be resolved by using both low exposure and high exposure in two separate exposure steps.