Camera Model: Laser L 3000 V4
Working Distance: 2900mm
Wooden Board Thickness: 15 mm
Wooden Board Dimensions: 1815 mm * 165mm
The wooden board has an uneven surface with irregular small indentations. After point cloud clustering, many points on the wooden board’s surface are filtered out, resulting in a significant loss of point cloud data on the wooden board.
Here are some historical insights and experiences:
-
Segmentation from Depth Map:
Start segmentation from the depth map. -
Reduce Camera Smoothing:
Lower the camera’s smoothing intensity slightly. -
Adjust Nearest Neighbor Search Radius:
When performing point cloud algorithms, consider reducing the nearest neighbor search radius to make edge normal gradients more pronounced. -
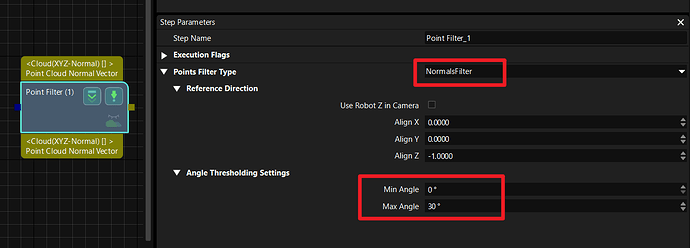
Coordinate Transformation for Normal Filtering:
When using normal filtering, adjust the reference direction by first establishing a coordinate system with a large planar surface (e.g., the ground). Transform the point cloud into this coordinate system. This will correct the point cloud’s orientation, making subsequent normal-based filtering more accurate. -
Edge Detection for Improved Clustering:
If clustering results are suboptimal, consider using 3D edge detection. Remove the edge points from the overall point cloud before clustering.
These experiences and tips can help enhance the accuracy and effectiveness of your point cloud processing and segmentation tasks.